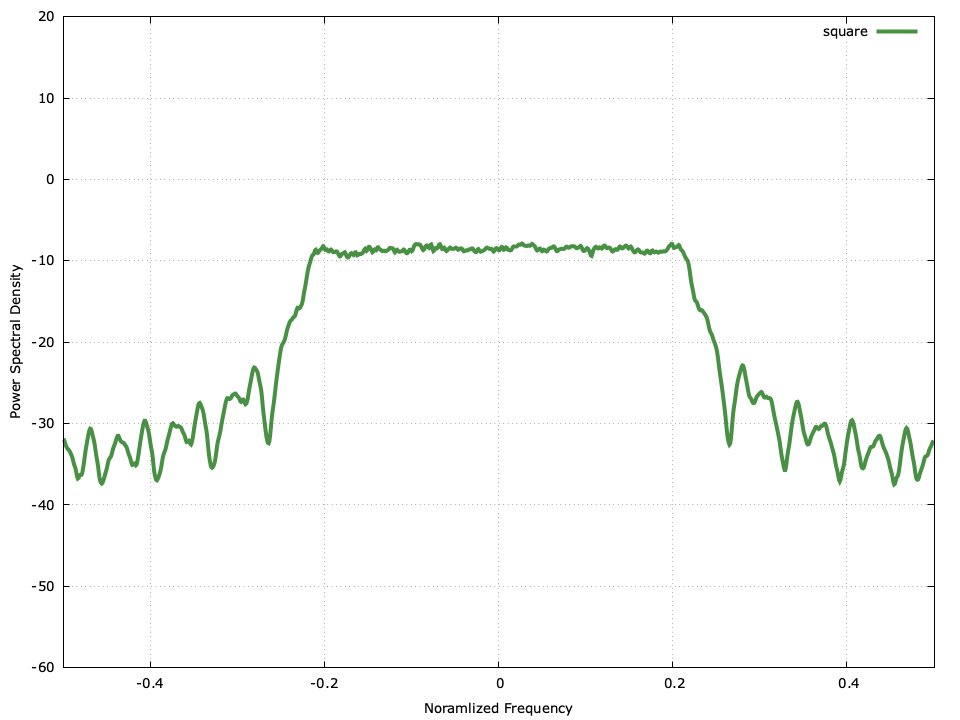
Frequency-shift keying (fsk) modem...
Theory of Operations∞
Interface∞
Listed below is the full interface to...
Here is a basic example of...
//
// fskmodem_example.c
//
// This example demostrates the M-ary frequency-shift keying
// (MFSK) modem in liquid. A message signal is modulated and the
// resulting signal is recovered using a demodulator object.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <liquid/liquid.h>
#define OUTPUT_FILENAME "fskmodem_example.m"
// print usage/help message
void usage()
{
printf("fskmodem_example -- frequency-shift keying example\n");
printf("options:\n");
printf(" h : print help\n");
printf(" m : bits/symbol, default: 1\n");
printf(" k : samples/symbol, default: 2*2^m\n");
printf(" b : signal bandwidth default: 0.2\n");
printf(" n : number of data symbols, default: 80\n");
printf(" s : SNR [dB], default: 40\n");
}
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
// options
unsigned int m = 3; // number of bits/symbol
unsigned int k = 0; // filter samples/symbol
unsigned int num_symbols = 8000; // number of data symbols
float SNRdB = 40.0f; // signal-to-noise ratio [dB]
float bandwidth = 0.20; // frequency spacing
unsigned int nfft = 1200; // FFT size for compute spectrum
int dopt;
while ((dopt = getopt(argc,argv,"hm:k:b:n:s:")) != EOF) {
switch (dopt) {
case 'h': usage(); return 0;
case 'm': m = atoi(optarg); break;
case 'k': k = atoi(optarg); break;
case 'b': bandwidth = atof(optarg); break;
case 'n': num_symbols = atoi(optarg); break;
case 's': SNRdB = atof(optarg); break;
default:
exit(1);
}
}
unsigned int i;
unsigned int j;
// derived values
if (k == 0)
k = 2 << m; // set samples per symbol if not otherwise specified
unsigned int M = 1 << m;
float nstd = powf(10.0f, -SNRdB/20.0f);
// validate input
if (k < M) {
fprintf(stderr,"errors: %s, samples/symbol must be at least modulation size (M=%u)\n", __FILE__,M);
exit(1);
} else if (k > 2048) {
fprintf(stderr,"errors: %s, samples/symbol exceeds maximum (2048)\n", __FILE__);
exit(1);
} else if (M > 1024) {
fprintf(stderr,"errors: %s, modulation size (M=%u) exceeds maximum (1024)\n", __FILE__, M);
exit(1);
} else if (bandwidth <= 0.0f || bandwidth >= 0.5f) {
fprintf(stderr,"errors: %s, bandwidht must be in (0,0.5)\n", __FILE__);
exit(1);
}
// create modulator/demodulator pair
fskmod mod = fskmod_create(m,k,bandwidth);
fskdem dem = fskdem_create(m,k,bandwidth);
fskdem_print(dem);
//
float complex buf_tx[k]; // transmit buffer
float complex buf_rx[k]; // transmit buffer
// spectral periodogram
spgramcf periodogram = spgramcf_create_default(nfft);
// modulate, demodulate, count errors
unsigned int num_symbol_errors = 0;
for (i=0; i<num_symbols; i++) {
// generate random symbol
unsigned int sym_in = rand() % M;
// modulate
fskmod_modulate(mod, sym_in, buf_tx);
// add noise
for (j=0; j<k; j++)
buf_rx[j] = buf_tx[j] + nstd*(randnf() + _Complex_I*randnf())*M_SQRT1_2;
// demodulate
unsigned int sym_out = fskdem_demodulate(dem, buf_rx);
// count errors
num_symbol_errors += (sym_in == sym_out) ? 0 : 1;
// estimate power spectral density
spgramcf_write(periodogram, buf_rx, k);
}
printf("symbol errors: %u / %u\n", num_symbol_errors, num_symbols);
// compute power spectral density of received signal
float psd[nfft];
spgramcf_get_psd(periodogram, psd);
spgramcf_destroy(periodogram);
//
// export results
//
FILE * fid = fopen(OUTPUT_FILENAME,"w");
fprintf(fid,"%% %s : auto-generated file\n", OUTPUT_FILENAME);
fprintf(fid,"clear all\n");
fprintf(fid,"close all\n");
fprintf(fid,"k = %u;\n", k);
fprintf(fid,"M = %u;\n", M);
fprintf(fid,"num_symbols = %u;\n", num_symbols);
fprintf(fid,"nfft = %u;\n", nfft);
// save power spectral density
fprintf(fid,"psd = zeros(1,nfft);\n");
for (i=0; i<nfft; i++)
fprintf(fid,"psd(%4u) = %12.8f;\n", i+1, psd[i]);
// plot PSD
fprintf(fid,"figure('Color','white');\n");
fprintf(fid,"f = [0:(nfft-1)]/nfft - 0.5;\n");
fprintf(fid,"plot(f,psd,'LineWidth',1.5,'Color',[0.5 0 0]);\n");
fprintf(fid,"axis([-0.5 0.5 -40 20]);\n");
fprintf(fid,"xlabel('Normalized Frequency [f/F_s]');\n");
fprintf(fid,"ylabel('PSD [dB]');\n");
fprintf(fid,"grid on;\n");
fclose(fid);
printf("results written to '%s'\n", OUTPUT_FILENAME);
return 0;
}