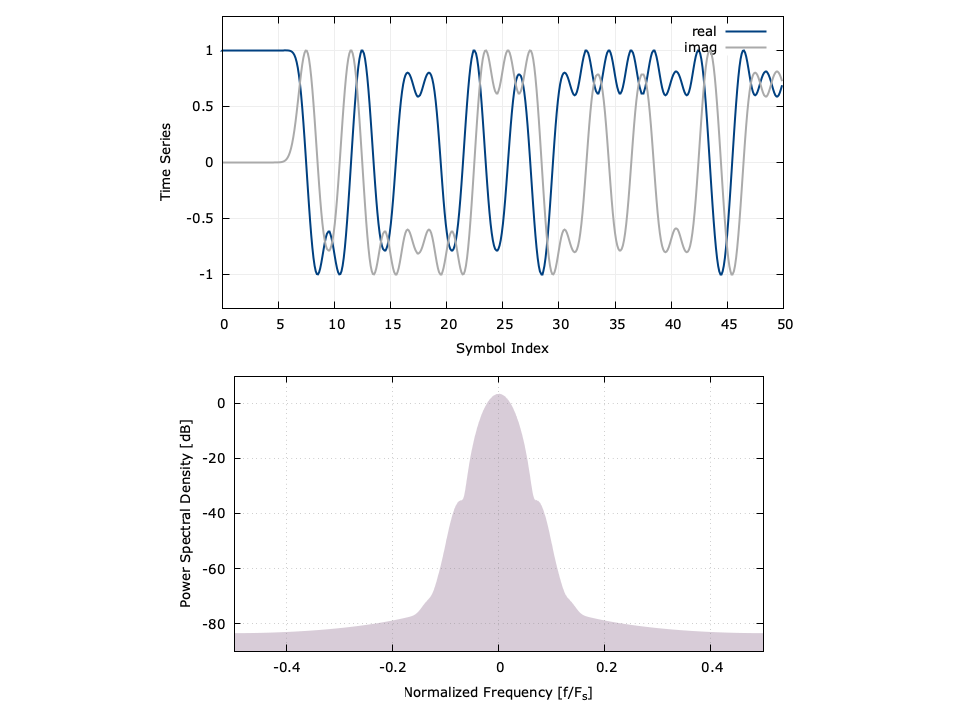
The two objects gmksmod and gmskdem implement the Gauss minimum-shift keying (GMSK) modem in liquid . Notice that unlike the linear modem objects, the GMSK modulator and demodulator are split into separate objects. Because GMSK is a nonlinear modulation scheme, the data are tied directly to the modulated waveform, resulting in separate modulator and demodulator objects.
Modulation is performed by interpolating the input data symbols with a transmit filter to provide an instantaneous frequency. This frequency is then integrated to provide an instantaneous phase, the resulting signal is used to generate the complex sinusoid for transmission.
Demodulation is performed by differentiating the instantaneous received frequency and running the resulting time-varying phase through a matched filter . By design, the GMSK transmit filter imparts inter-symbol interference (by nature of the pulse shape). To mitigate symbol errors, the receive filter is initially designed to remove as much ISI as possible
Listed below is an example to interfacing with the gmskmod and gmskdem modulator/demodulator objects. Notice that in the example, the output data symbols match the input only when accounting for the delay in the modulator/demodulator filters.
#include <liquid/liquid.h>
int main() {
// options
unsigned int k = 10; // filter samples/symbol
unsigned int m = 7; // filter delay (symbols)
float BT = 0.25f; // bandwidth-time product
unsigned int nsyms = 30; // number of symbols
// create modulator/demodulator objects
gmskmod mod = gmskmod_create(k, m, BT);
gmskdem demod = gmskdem_create(k, m, BT);
// derived values
unsigned int delay = 2 * m; // delay between mod/demod
unsigned int syms_in [nsyms]; // input data symbol
unsigned int syms_out[nsyms]; // input data symbol
float complex buf[k]; // modulated samples
// pre-generate symbols
unsigned int i;
for (i=0; i<nsyms; i++)
syms_in[i] = rand() & 1;
// run through modulator/demodulator
for (i=0; i<nsyms; i++)
{
// modulate symbol and store samples into buffer
gmskmod_modulate(mod, syms_in[i], buf);
// demodulate
gmskdem_demodulate(demod, buf, syms_out+i);
// print result *accounting for delay*
printf("[%2u] out=%1u", i, syms_out[i]);
if (i >= delay)
printf(" : in=%1u\n", syms_in[i-delay]);
else
printf("\n");
}
// destroy modem objects
gmskmod_destroy(mod);
gmskdem_destroy(demod);
return 0;
}
Here is a time series and spectral estimate of the resulting signal: