Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Design using Parks-McClellan Algorithm¶
FIR filter design using the Parks-McClellan algorithm is implemented in
liquid with the firdespm interface.
The Parks-McClellan algorithm uses the Remez exchange algorithm to solve
the minimax problem (minimize the maximum error) for filter design.
The interface accepts a description of \(N_b\) disjoint and
non-overlapping frequency bands with a desired response and relative
error weighting for each, and computes the resulting filter
coefficients.
int firdespm_run(unsigned int _h_len,
unsigned int _num_bands,
float * _bands,
float * _des,
float * _weights,
liquid_firdespm_wtype * _wtype,
liquid_firdespm_btype _btype,
float * _h);
_bandsis a \([N_b \times 2]\) matrix of the band edge descriptions. Each row corresponds to an upper and lower band edge for each region of interest. These regions cannot be overlapping._desis an array of size \(N_b\) with the desired response (linear) for each band._weightsis an array of size \(N_b\) with the relative error weighting for each band._num_bandsrepresents \(N_b\), the number of bands in the design._btypegives the filter type for the design. This is typicallyLIQUID_FIRDESPM_BANDPASSfor the majority of filters._wtypeis an array of length \(N_b\) which specifies the weighting function for each band (flat, exponential, or linear).
Example¶
Listed below is an example of the firdespm interface.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "liquid.h"
int main(int argc, char*argv[]) {
// options
unsigned int n = 101; // filter length
liquid_firdespm_btype btype = LIQUID_FIRDESPM_BANDPASS;
unsigned int num_bands = 4;
float bands[8] = {0.00f, 0.10f, // 1
0.12f, 0.29f, // 0
0.30f, 0.40f, // 0.1
0.41f, 0.50f}; // 0
float des[4] = {1.0f, 0.0f, 0.1f, 0.0f};
float weights[4] = {1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f};
liquid_firdespm_wtype wtype[4] = {LIQUID_FIRDESPM_FLATWEIGHT,
LIQUID_FIRDESPM_FLATWEIGHT,
LIQUID_FIRDESPM_FLATWEIGHT,
LIQUID_FIRDESPM_FLATWEIGHT};
float h[n];
firdespm_run(n,num_bands,bands,des,weights,wtype,btype,h);
printf("w\n");
unsigned int i;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
printf("%12.8f\n",h[i]);
return 0;
}
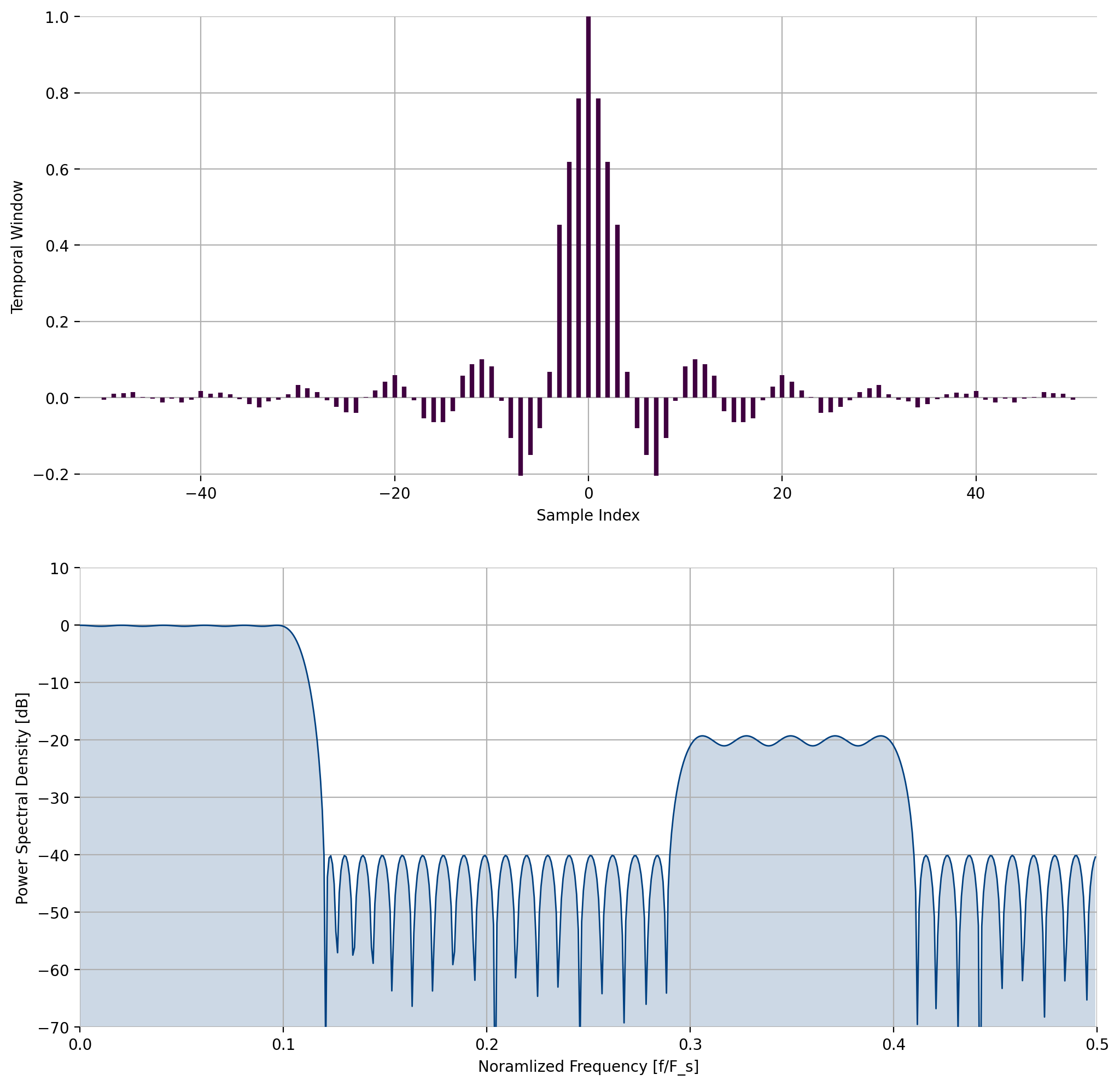
Figure 6 Example of firdespm¶