Continuous-Phase Frequency-Shift Keying (CPFSK) Modem¶
Shown in Figure 28 below is a compaarison of the transmitted spectrum for various combinations of parameters.
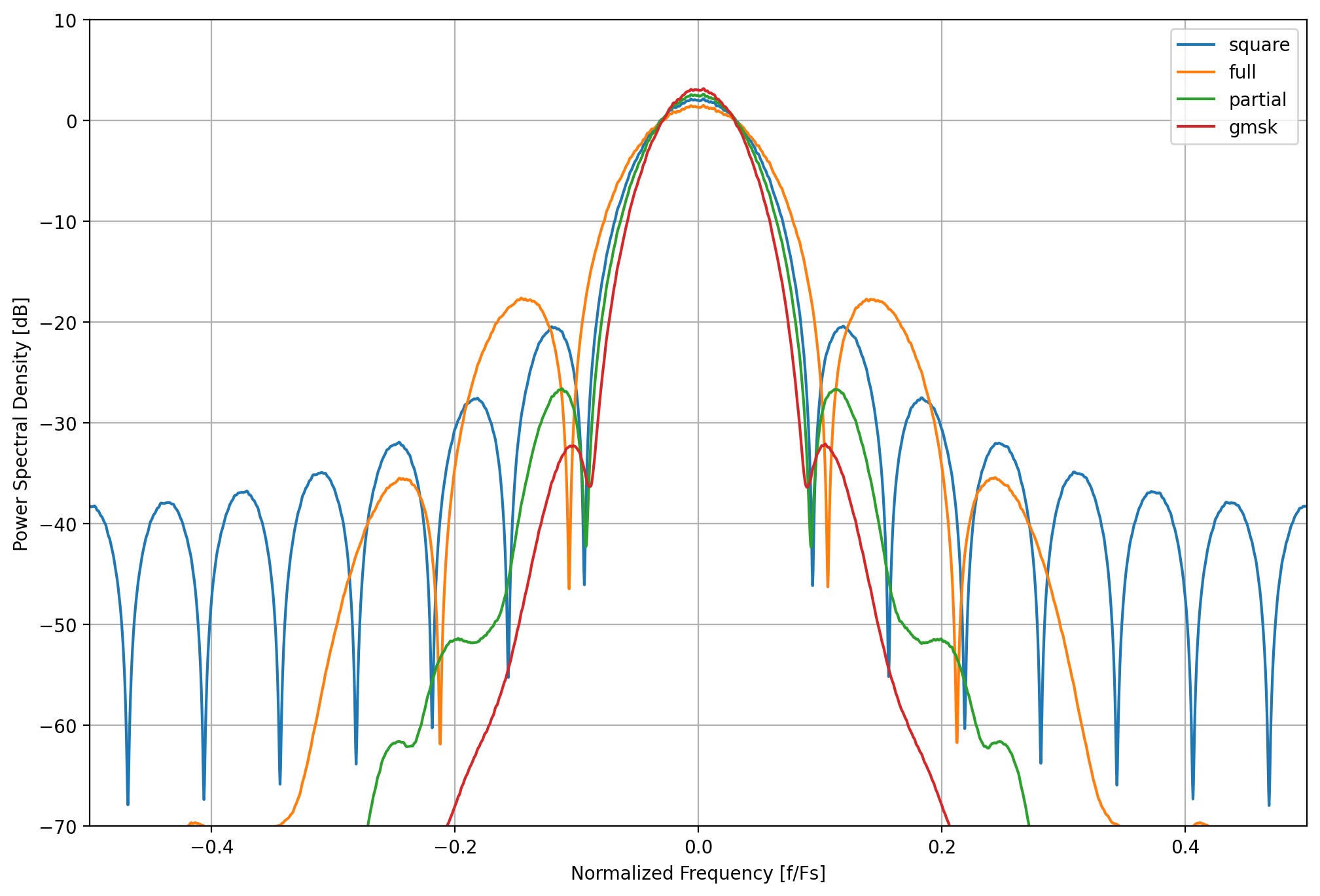
Figure 28 Power spectral density of different CPFSK modem types with \(k=8\) samples per symbol¶
Interface¶
Here is a basic example of the cpfksmod and cpfskdem objects.
// demonstrate interface to cpfskmod and cpfskdem objects
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <liquid/liquid.h>
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
// options
unsigned int bps = 1; // number of bits/symbol
float h = 0.5f; // modulation index (h=1/2 for MSK)
unsigned int k = 4; // filter samples/symbol
unsigned int m = 3; // filter delay (symbols)
float beta = 0.35f; // filter bandwidth-time product
int filter_type = LIQUID_CPFSK_SQUARE; // filter type
// create modem objects
cpfskmod mod = cpfskmod_create(bps, h, k, m, beta, filter_type);
cpfskdem dem = cpfskdem_create(bps, h, k, m, beta, filter_type);
// arrays
unsigned int i;
unsigned int M = 1 << bps; // constellation size
float complex buf[k]; // sample buffer
for (i=0; i<20; i++) {
// generate random message signal
unsigned int sym_in = rand() % M;
// modulate signal
cpfskmod_modulate(mod, sym_in, buf);
// demodulate signal
unsigned int sym_out = cpfskdem_demodulate(dem, buf);
}
// destroy modem objects
cpfskmod_destroy(mod);
cpfskdem_destroy(dem);
return 0;
}